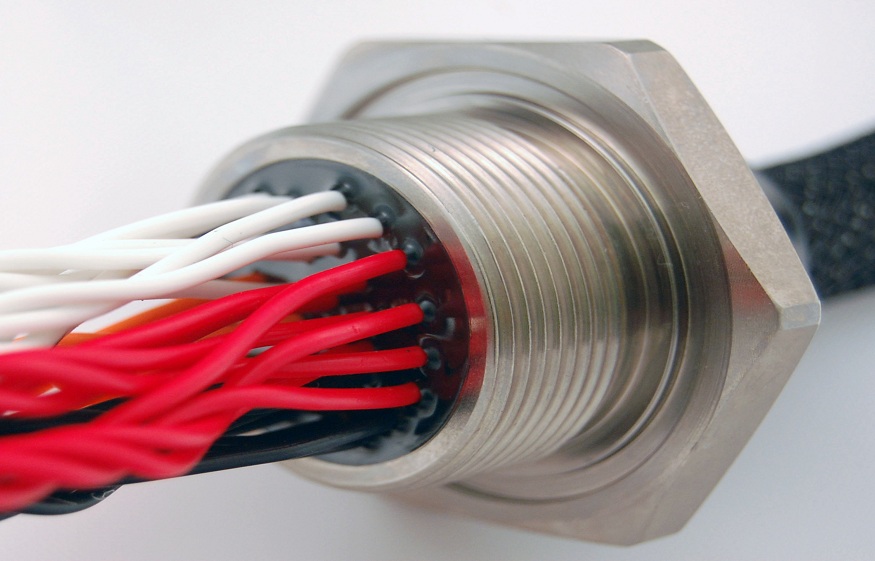
Hermetic feedthroughs are essential components in modern electronics, industrial equipment, medical devices, and aerospace systems. They provide a sealed interface that allows electrical, optical, or fluid connections to pass through a barrier without compromising the internal environment. This buyer’s guide explains everything you need to know about hermetic feedthroughs, including types, applications, materials, and selection tips.
What Is a Hermetic Feedthrough?
A hermetic feedthrough is a device that maintains a leak-proof seal while allowing a connection to pass through it. This ensures sensitive equipment is protected from air, moisture, or contaminants. Hermetic feedthroughs are critical in high-vacuum systems, medical devices, industrial automation, and aerospace technology, where environmental integrity and electrical performance are crucial.
Common Types of Hermetic Feedthroughs
Understanding the types of hermetic feedthroughs helps buyers select the right product for their application.
- Glass-to-Metal Feedthroughs: These consist of metal pins fused in a glass insulator, bonded to a metal housing. They are ideal for high-vacuum applications and electrical insulation.
- Ceramic-to-Metal Feedthroughs: These use a ceramic insulator fused to metal, providing superior durability, thermal resistance, and mechanical strength.
- Coaxial Feedthroughs: Designed for RF or microwave signals, coaxial feedthroughs maintain impedance control while ensuring hermetic sealing.
- Multi-Pin Feedthroughs: Multiple insulated pins pass through a single sealed barrier, saving space and simplifying wiring.
- High-Voltage Feedthroughs: Engineered to safely handle high-voltage signals while maintaining airtight integrity.
- Optical Feedthroughs: Allow fiber optic signals to pass through hermetic barriers without loss or contamination.
Materials Used in Hermetic Feedthroughs
Material selection directly affects the performance and reliability of a feedthrough:
- Metals: Stainless steel, Kovar, or titanium for strength, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with vacuum sealing.
- Glass: Provides excellent electrical insulation and vacuum sealing for glass-to-metal feedthroughs.
- Ceramic (Alumina): Used in ceramic-to-metal feedthroughs for high temperature, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation.
- Polymers (Limited Use): Occasionally used for low-stress, non-critical applications, but metals and ceramics remain standard in industrial and aerospace applications.
Key Applications of Hermetic Feedthroughs
Hermetic feedthroughs are widely used in industries that require reliable sealing and electrical or optical transmission:
- Industrial: Vacuum chambers, high-temperature furnaces, and process control systems.
- Aerospace & Defense: Satellites, radar systems, and high-reliability electronics.
- Medical Devices: Imaging systems, surgical instruments, and implantable devices.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Wafer processing equipment, plasma chambers, and cleanroom machinery.
- Scientific Instruments: Cryogenic systems, particle accelerators, and research laboratories.
Factors to Consider When Buying Hermetic Feedthroughs
Selecting the right hermetic feedthrough requires careful consideration:
- Type of Signal: Determine if the feedthrough will carry electrical, RF, high-voltage, or optical signals.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider temperature, pressure, vacuum, humidity, and exposure to corrosive materials.
- Number of Connections: Single-pin, multi-pin, or coaxial depending on your system requirements.
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the feedthrough can handle the required electrical load.
- Mechanical Strength: Resistance to vibration, shock, and thermal cycling is critical for industrial and aerospace applications.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure metals, glass, or ceramics are compatible with the operating environment.
- Certification and Standards: Look for feedthroughs that meet industry standards for aerospace, medical, or industrial compliance.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation ensures long-term reliability:
- Verify compatibility with the mounting flange or chamber.
- Use recommended torque values for screws to avoid cracks in glass or ceramic.
- Avoid mechanical stress that can compromise the hermetic seal.
- Periodically inspect seals in high-temperature or high-vibration applications.
- Keep feedthroughs clean and free from contaminants during installation.
Advantages of Using Hermetic Feedthroughs
Hermetic feedthroughs offer several benefits for industrial and high-reliability applications:
- Environmental Protection: Prevents contamination from air, moisture, or corrosive substances.
- Electrical Integrity: Maintains insulation and prevents short circuits.
- Durability: Resistant to extreme temperatures, pressure, and vibration.
- Space Efficiency: Multi-pin designs reduce wiring complexity.
- Reliability: Essential for high-stakes applications like aerospace and medical devices.
Conclusion
Hermetic feedthroughs are critical components for maintaining sealed environments while enabling electrical or optical connections. Choosing the right type, material, and configuration is essential for system reliability and performance. Whether you are designing industrial machinery, aerospace electronics, or medical devices, understanding the features and applications of hermetic feedthroughs ensures you make informed buying decisions.
By carefully evaluating your operational environment, signal requirements, and mechanical needs, you can select a hermetic feedthrough that provides long-term reliability and maximum protection for your equipment.